Configuring the Runtime Environment for Java Desktop Application Support
This section explains runtime configuration procedures that need to be done to support JIA automation for Java desktop applications.
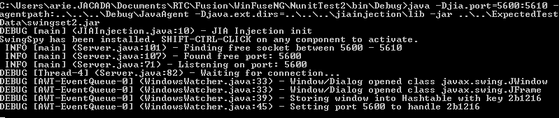
To be able to run JIA automation, you need to run Java from the command line with the following down string:
Java.exe -agentpath:JavaAgent -Djava.ext.dirs=<extension dirs> -Djia.port=xxxx:yyyy -jar "DesiredJarPath"
•-agentpath: The full path location of the JavaAgent.dll. This .dll file bootstraps the entire initialization procedure for JIA automation. The file should be located directly under the JIA installation directory.
•-Djava.ext.dirs: The location of various Java files (mostly .jar) that support Java automation for JIA. Direct this parameter to the JavaSupport directory under the JIA installation directory.
•-Djia.port: Range of ports that will be used by JIA runtime to initialize Java applications. When this parameter is omitted, the default range is 4444-4460. Each Java application started uses a free port within this port range.
If desired, you can use a single port. In this case, the range consists of the single port specified.
Minimally, the command line should contain -agentpath and -Djava.ext.dirs.
The following figure shows an example of an application run with the configured parameters.
Java Network Launching Protocol (JNLP) is a protocol that specifies how to launch Java web start applications (i.e., applications that start from a web browser). To support these Java applications in JIA (and to be able to use the Java spy tool), virtual machine options such as the agent path, external directories or port range need to be specified. To support these virtual machine options for JNLP, the environment variable JAVAWS_VM_ARGS needs to be set (in the System variables frame) as follows:
For example:
After setting the environment variable, you can create a batch file for runtime configuration. The following example shows a batch file that runs a Java Notepad application:
|